VA Whistleblowers: Retaliation Claim Investigations and Settlement Agreements [Reissued with revisions on Oct. 27, 2023]
Fast Facts
Federal employees who are whistleblowers can help fight fraud, waste, and abuse, so laws protect them from retaliation, such as demotion and firing.
We're looking into whistleblower retaliation cases at the Department of Veterans Affairs. This testimony covers our prior and ongoing work.
Amid an uptick in all cases reported to the VA, whistleblower retaliation cases have increased from 577 in FY 2020 to 736 in FY 2023.
In cases reported to the federal Office of Special Counsel from FY 2018-22:
The percentage of cases that closed in the whistleblower's favor increased
Less than 1% of these cases were closed with a settlement agreement

Revised October 27, 2023 to correct figures 2, 3, and 4 and to revise rescheduled hearing date. The corrected figure 2 should show the volume of Office of Accountability and Whistleblower Protection (OAWP) cases for fiscal years 2020-2023. The corrected figure 3 should show the volume of Office of Special Counsel (OSC) cases Involving Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees for fiscal years 2018-2022. The corrected figure 4 should show the median case length for OSC investigations involving VA employees for fiscal years 2018-2022.
Highlights
What GAO Found
The number of whistleblower retaliation cases that the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Accountability and Whistleblower Protection (OAWP) has received increased since fiscal year 2020. The number of other cases also increased. Specifically, OAWP received 577 whistleblower retaliation cases in fiscal year 2020 and 736 in fiscal year 2023. The non-whistleblower retaliation cases that OAWP received increased from 1,594 in fiscal year 2020 to 1,972 in fiscal year 2023.
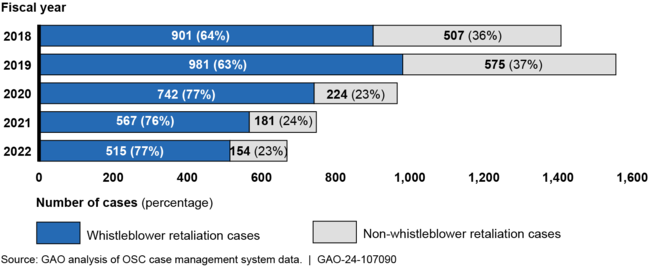
Office of Special Counsel (OSC) investigations of allegations of whistleblower retaliation from VA employees have decreased in number and have increasingly closed with a favorable action that benefits the complainant (i.e., whistleblower). Most OSC investigations of complaints from VA employees included allegations of whistleblower retaliation. From fiscal years 2018 through 2022, 69 percent of OSC cases involving VA employees included allegations of whistleblower retaliation. Specifically, OSC received 901 whistleblower retaliation cases involving VA in fiscal year 2018 and 515 in fiscal year 2022 (see figure). The percentage of these cases with a favorable action increased from 3 percent to 10 percent.
Volume of Office of Special Counsel (OSC) Cases Involving Department of Veterans Affairs Employees, Fiscal Years 2018–2022
According to VA OGC officials, the settlement agreement process involves three distinct phases: initiation, negotiation, and monitoring. VA and a complainant can settle claims of whistleblower retaliation in the office where a dispute arises at any point in the complaint process. The agency has settled 71 whistleblower retaliation cases since it began tracking them in 2022. OAWP tracking information showed that most of the settlements included monetary awards for the whistleblower, ranging from about $1,800 to 525,000. In addition, the settlement may also have included salary adjustments or back-pay. OAWP information also showed that complaints come from program offices across the agency, but most of the settlements originate from complaints out of VA's Veteran's Health Administration, the largest of VA's three administrations.
Why GAO Did This Study
Whistleblowers can help protect the public interest by reporting allegations of wrongdoing, such as a violation of law or gross mismanagement. While whistleblowers potentially safeguard the government from fraud, waste, and abuse, they may risk reprisal from their agencies for disclosures, such as demotion, reassignment or termination.
VA is one of the largest federal agencies and employs around 400,000 people across hundreds of medical facilities, clinics, and benefits offices. Whistleblowers at the VA can file complaints of retaliation internally, through the agency's OAWP, or externally with other agencies, such as OSC. In some cases, whistleblowers will enter into a settlement agreement with VA to resolve the dispute.
This testimony summarizes GAO's May 2023 report on VA whistleblower retaliation claims and settlements, as well as preliminary observations from related ongoing work. Specifically, this testimony examines: 1) the characteristics of OAWP whistleblower retaliation investigations, 2) the characteristics of OSC whistleblower retaliation investigations, and 3) how VA resolves such allegations through settlement agreements.
GAO reviewed OSC and VA documents, interviewed agency officials, analyzed OSC case management system data from fiscal years 2018-22, which were the most recent data at the time of the report. In addition, as part of our ongoing work, we collected additional information on whistleblower retaliation claims and settlements from OAWP's Matter Tracking System.
For more information, contact Thomas Costa at (202) 512-4769 or costat@gao.gov.
