Enterprise Risk Management: Selected Agencies' Experiences Illustrate Good Practices in Managing Risk
Fast Facts
Federal managers often handle complex and risky missions, such as preparing for and responding to natural disasters, and building and managing safe transportation systems. While it is not possible to eliminate all uncertainties in these types of projects, there are strategies that can help plan and manage them.
One such strategy is Enterprise Risk Management. It provides ways to better anticipate and manage risk across an agency. Our enterprise risk management framework has 6 essential elements to consider when implementing ERM, as shown below. We also identified good practices, as well as examples from federal agencies that are using ERM.
Essential Elements of Federal Government Enterprise Risk Management

A circle graph of the 6 elements of federal enterprise risk management.
Highlights
What GAO Found
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a forward-looking management approach that allows agencies to assess threats and opportunities that could affect the achievement of its goals. While there are a number of different frameworks for ERM, the figure below lists essential elements for an agency to carry out ERM effectively. GAO reviewed its risk management framework and incorporated changes to better address recent and emerging federal experience with ERM and identify the essential elements of ERM as shown below.
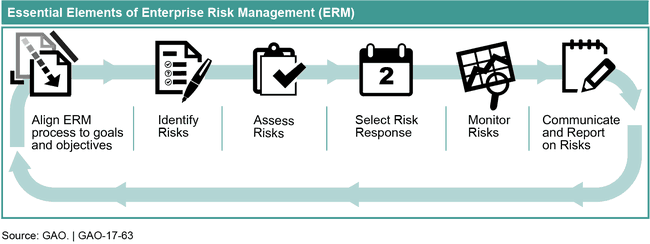
GAO has identified six good practices to use when implementing ERM.
Essential Elements and Good Practices of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
|
Elements |
Good Practices |
|
Align ERM process to goals and objectives |
Leaders Guide and Sustain ERM Strategy Implementing ERM requires the full engagement and commitment of senior leaders, supports the role of leadership in the agency goal setting process, and demonstrates to agency staff the importance of ERM. |
|
Identify Risks |
Develop a Risk-Informed Culture to Ensure All Employees Can Effectively Raise Risks Developing an organizational culture to encourage employees to identify and discuss risks openly is critical to ERM success. |
|
Assess Risks |
Integrate ERM Capability to Support Strategic Planning and Organizational Performance Management Integrating the prioritized risk assessment into strategic planning and organizational performance management processes helps improve budgeting, operational, or resource allocation planning. |
|
Select Risk Response |
Establish a Customized ERM Program Integrated into Existing Agency Processes Customizing ERM helps agency leaders regularly consider risk and select the most appropriate risk response that fits the particular structure and culture of an agency. |
|
Monitor Risks |
Continuously Manage Risks Conducting the ERM review cycle on a regular basis and monitoring the selected risk response with performance indicators allows the agency to track results and impact on the mission, and whether the risk response is successful or requires additional actions. |
|
Communicate and Report on Risks |
Share Information with Internal and External Stakeholders to Identify and Communicate Risks Sharing risk information and incorporating feedback from internal and external stakeholders can help organizations identify and better manage risks, as well as increase transparency and accountability to Congress and taxpayers. |
Source: GAO. | GAO-17-63
Why GAO Did This Study
Federal leaders are responsible for managing complex and risky missions. ERM is a way to assist agencies with managing risk across the organization. In July 2016, the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) issued an updated circular requiring federal agencies to implement ERM to ensure federal managers are effectively managing risks that could affect the achievement of agency strategic objectives.
GAO's objectives were to (1) update its risk management framework to more fully include evolving requirements and essential elements for federal enterprise risk management, and (2) identify good practices that selected agencies have taken that illustrate those essential elements.
GAO reviewed literature to identify good ERM practices that generally aligned with the essential elements and validated these with subject matter specialists.
GAO also interviewed officials representing the 24 Chief Financial Officer (CFO) Act agencies about ERM activities and reviewed documentation where available to corroborate officials' statements. GAO studied agencies' practices using ERM and selected examples that best illustrated the essential elements and good practices of ERM.
GAO provided a draft of this report to OMB and the 24 CFO Act agencies for review and comment. OMB generally agreed with the report. Of the CFO act agencies, 12 provided technical comments, which GAO included as appropriate; the others did not provide any comments.
For more information, contact J. Christopher Mihm at (202) 512-6806 or mihmj@gao.gov.
