Artificial Intelligence: Generative AI's Environmental and Human Effects
Fast Facts
Generative AI could dramatically increase productivity and transform workloads in many industries. It can be used to respond to questions in customer service chats, create schedules, summarize information, produce Internet content—and more.
But generative AI also poses potential risks to people and the environment.
For example, the IT equipment that powers generative AI needs a lot of water and electricity to function efficiently and avoid overheating. Also, generative AI could replace workers or be used to create dangerous deepfakes.
Our Technology Assessment discusses these and other challenges and offers options for policymakers to consider.

Highlights
What GAO Found
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) could revolutionize entire industries. In the nearer term, it may dramatically increase productivity and transform daily tasks in many sectors. However, both its benefits and risks, including its environmental and human effects, are unknown or unclear.
Generative AI uses significant energy and water resources, but companies are generally not reporting details of these uses. Most estimates of environmental effects of generative AI technologies have focused on quantifying the energy consumed, and carbon emissions associated with generating that energy, required to train the generative AI model. Estimates of water consumption by generative AI are limited. Generative AI is expected to be a driving force for data center demand, but what portion of data center electricity consumption is related to generative AI is unclear. According to the International Energy Agency, U.S. data center electricity consumption was approximately 4 percent of U.S. electricity demand in 2022 and could be 6 percent of demand in 2026.
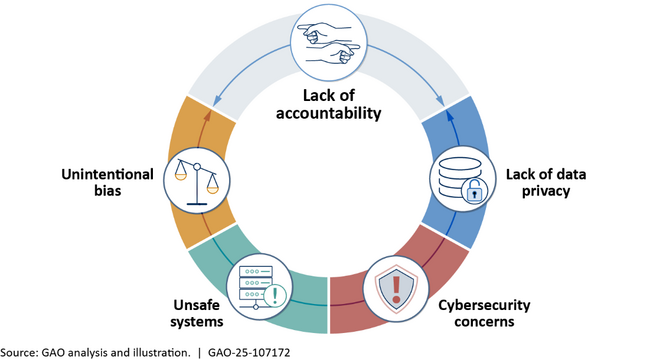
While generative AI may bring beneficial effects for people, GAO highlights five risks and challenges that could result in negative human effects on society, culture, and people from generative AI (see figure). For example, unsafe systems may produce outputs that compromise safety, such as inaccurate information, undesirable content, or the enabling of malicious behavior. However, definitive statements about these risks and challenges are difficult to make because generative AI is rapidly evolving, and private developers do not disclose some key technical information.
Selected generative artificial antelligence risks and challenges that could result in human effects
GAO identified policy options to consider that could enhance the benefits or address the challenges of environmental and human effects of generative AI. These policy options identify possible actions by policymakers, which include Congress, federal agencies, state and local governments, academic and research institutions, and industry. In addition, policymakers could choose to maintain the status quo, whereby they would not take additional action beyond current efforts. See below for details on the policy options.
Policy options that could enhance the benefits or address the challenges of environmental and human effects of generative artificial intelligence (AI).
| Policy Option | Example implementation approaches | Opportunities and considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 4.1 Environmental Effects | ||
| Maintain status quo (report page 29) |
|
|
| Improve data collection and reporting (report page 29) |
|
|
| Encourage innovation (report page 30) |
|
|
| 4.2 Human Effects | ||
| Maintain status quo (report page 30) |
|
|
| Encourage use of AI frameworks (report page 31) |
|
|
| Share best practices and establish standards (report page 32) |
|
|
Source: GAO. | GAO-25-107172
Why GAO Did This Study
Generative AI uses large amounts of energy and water. Additionally, generative AI may displace workers, help spread false information, and create or elevate risks to national security. The benefits and risks of generative AI are unclear, and estimates of its effects are highly variable because of a lack of available data. The continued growth of generative AI products and services raises questions about the scale of benefits and risks.
GAO was asked to conduct a technology assessment of generative AI effects, particularly its risks. GAO examined: (1) potential environmental effects of generative AI technologies, (2) potential human effects of generative AI technologies, and (3) what policy options exist to enhance the benefits or mitigate the environmental and human effects of generative AI technologies
For more information, contact Brian Bothwell at BothwellB@gao.gov or Kevin Walsh at WalshK@gao.gov.
