NASA Lunar Programs: Improved Mission Guidance Needed as Artemis Complexity Grows
Fast Facts
NASA is embarking on a series of missions—collectively known as Artemis—that will return astronauts to the moon and ultimately bring humans to Mars over the next decade-plus.
The guidance NASA uses to create and manage Artemis mission schedules was intended for individual programs, not missions. Missions integrate several programs together and require coordination across different NASA divisions and with contractors. Schedule guidance specifically for missions would help NASA coordinate integration activities, as Artemis missions will involve more programs over time.
Our recommendations include creating mission schedule guidance.
Artist Rendition of Astronauts Conducting Research on the Moon

Highlights
What GAO Found
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) plans to conduct Artemis missions—a series of missions that will return astronauts to the moon, build a sustainable lunar presence, and ultimately bring humans to Mars—into the 2030s.
Artemis Missions and the Number of Programs Needed for Each Mission
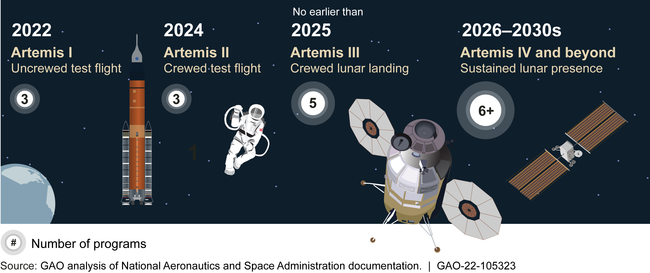
To do this, NASA will need to develop, acquire, and integrate a number of new systems. NASA has made progress on integration and risk management for the first lunar landing mission, Artemis III. For example, NASA established integration processes, roles, and responsibilities, and recently took additional steps to manage risks for the series of missions.
NASA, however, does not yet have guidance for creating or managing Artemis mission schedules that will help integrate the individual programs required for launch. NASA is using existing schedule management guidance developed for individual programs, not multi-program missions. Without guidance specifically for multi-program missions, NASA lacks reasonable assurance it has consistent schedule management practices in place for the Artemis schedules. Schedule management guidance would also assist coordination, which will be increasingly necessary as the Artemis missions will involve more programs over time and therefore become more complex.
NASA conducts workforce planning through the programs that comprise the Artemis missions across the next 5 budget years. NASA faces uncertainties beyond that horizon that have hindered longer-term planning. However, NASA is committing billions of dollars in development and production contracts for future Artemis missions that extend into the 2030s. This will require an extensive workforce to execute. Prior GAO work found that other agencies facing uncertainty assessed a range of future options, known as scenario planning, which provided flexibility to determine future workforce needs. In May 2022, NASA officials said they were examining the use of scenario planning to help future workforce planning efforts. But they have not yet completed or implemented guidance to do so. As NASA begins to execute the first of many Artemis missions, it has the opportunity to use scenario planning to inform future workforce environments it may face and address broader workforce challenges.
Why GAO Did This Study
In May 2021, GAO found that NASA faced many challenges to its ambitious goal of returning astronauts to the moon by 2024. Subsequently, NASA delayed the planned lunar landing, known as Artemis III, to no earlier than 2025. Artemis III is one in a planned series of missions to eventually establish a sustainable lunar presence and a path to Mars over the next decade-plus. Successfully executing these missions requires extensive coordination across several NASA programs and with a wide range of contractors to ensure systems operate together seamlessly and safely.
A House report to an appropriations bill included a provision for GAO to review NASA's proposed lunar-focused programs. This report assesses the extent to which NASA (1) is managing mission integration risks; (2) developed Artemis mission-level schedules; and (3) assessed the ability of the Artemis workforce to manage and oversee lunar landing missions.
GAO reviewed relevant NASA documents, schedules, and plans and interviewed NASA headquarters and center officials.
Recommendations
GAO is making four recommendations, including that NASA develop Artemis mission-level schedule management guidance and develop guidance on conducting Artemis workforce scenario planning. NASA concurred with all four of the recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration | The NASA Administrator should ensure that the Chief Financial Officer, in coordination with the mission directorates, develops Artemis mission-level schedule management guidance. (Recommendation 1) |
NASA agreed with this recommendation. In March 2024, the Office of the Chief Financial Officer finalized updates to the NASA Schedule Management Handbook. NASA provided the updated Schedule Management Handbook to GAO in July 2024. The updates included guidance for developing schedule management plans for multi-mission campaigns, which consist of a series of missions that combine program capabilities. This guidance could apply to Artemis missions, as NASA relies on several program capabilities to execute each Artemis mission.
|
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration | The NASA Administrator, in coordination with the relevant mission directorates, should ensure that NASA conducts a schedule risk analysis for the Artemis II mission as close as possible to completion of the Artemis I mission and update it as needed to incorporate schedule updates and new risks. (Recommendation 2) |
NASA agreed with this recommendation. In September 2023, NASA completed a schedule risk analysis for the Artemis II mission. As a result of the schedule risk analysis, in December 2024, NASA announced an updated launch readiness date of no later than April 2026 for the mission. In September 2025, mission directorate officials said that they did not plan to conduct any additional schedule risk analyses for the Artemis II mission as they are continuing to work towards executing the mission by no later than April 2026.
|
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration | The NASA Administrator, in coordination with the relevant mission directorates for Artemis III and later missions, should ensure that NASA develops guidance for division-level schedule collaboration including setting expectations for data sharing and the type(s) of data required. (Recommendation 3) |
NASA agreed with this recommendation. In July 2022, NASA released guidance for division-level collaboration on methodologies, techniques, and tools within the Artemis Campaign Division Schedule Management Plan. This plan includes documentation of how the Division will work across programs and other organizations to share data. The agency finalized the plan in July 2022 and provided it to GAO in September 2022.
|
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration | The NASA Administrator should ensure that the Office of the Chief Human Capital Officer develops guidance that identifies a regular and recurring process for long-term Artemis workforce scenario planning to address future uncertainties, at least 5 years beyond the existing 5-year workforce plans. (Recommendation 4) |
NASA agreed with this recommendation. In February 2022, NASA issued its Strategic Workforce Planning policy. Subsequently, in May 2022, NASA issued a memo to the Centers on Workforce Forecasting and Strategic Planning Process for Mission Workforce. This memo directed Centers to include workforce planning information in the near-term (1-5 years) and long term (5 years and beyond) in their annual workforce plans. In September 2023, NASA Centers developed annual workforce plans that implemented NASA guidance for long term planning and provided these plans to GAO in July 2024.
|
