NASA: Assessments of Major Projects
Fast Facts
NASA plans to invest over $80 billion in its major projects to continue exploring Earth, the moon, and the solar system. This is our 14th annual assessment of NASA's major projects.
In 2021, NASA completed six projects, including launching the James Webb space telescope. But, in the last year, NASA's major projects collectively exceeded their cost estimates by almost $3 billion. They also surpassed their collective schedules by almost 10 years. COVID-19 was not the primary cause of the cost growth and schedule delays, but exacerbated these challenges.
NASA's acquisition management is on our High Risk list.
Artist Rendition of Astronauts Conducting Research on the Moon

Highlights
What GAO Found
Continuing a recent trend, NASA's portfolio of major projects experienced significant cost and schedule overruns and more projects were added (see figure). Of the 21 major projects in the development phase of NASA's acquisition process (which includes building and launching the system), 15 were responsible for cumulative cost overruns of about $12 billion and cumulative schedule delays of 28 years. But just three projects—the James Webb Space Telescope, Space Launch System, and Orion—are responsible for more than three-quarters of the cost growth and almost half of the delays.
Cumulative Cost and Schedule Overruns for NASA's Major Projects in Development
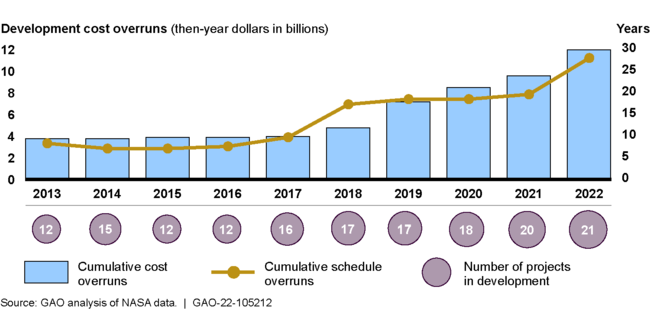
In the past year, the majority of NASA's projects in development increased their cost estimates, schedule estimates, or both. Technical issues and new scope were the primary causes of overruns. However, COVID-19 exacerbated these challenges with government and contractor facility shutdowns and remote work.
Current overruns and the risk of future COVID-19 issues could have a cascading effect on NASA's ability to manage its portfolio. NASA designates cost reserves to help projects address risks. However, when projects exhaust these reserves and need additional funding, it can limit the agency's ability to fund existing missions or start new ones. For example, NASA officials said some new projects are preparing for later launch dates due in part to funding limitations caused by other projects' cost overruns. NASA is taking steps to improve its portfolio management, but it is too soon to determine the results of these efforts.
Why GAO Did This Study
NASA plans to invest at least $80 billion in its major projects to continue exploring Earth, the moon, and the solar system. Major projects are those with costs of over $250 million. An explanatory statement included a provision for GAO to prepare status reports on NASA's major projects. This is GAO's 14th annual assessment.
This report describes the cost and schedule performance of NASA's major projects and GAO's assessment of these projects' technology development and design stability. The report also includes individual assessments of the major projects.
GAO collected and analyzed data; reviewed project status reports; and interviewed NASA officials. GAO reviewed projects in the formulation phase (which takes a project through its preliminary design), and those in the subsequent development phase.
Recommendations
In prior work, GAO made multiple recommendations to improve NASA's management of its major projects. NASA agreed with most of those recommendations and implemented many changes. However, as of March 2022, NASA had not fully addressed 23 recommendations—six of which have been awaiting actions for over 5 years.

