Foster Care: Additional Actions Could Help HHS Better Support States' Use of Private Providers to Recruit and Retain Foster Families
Highlights
What GAO Found
States employ a range of strategies to recruit foster families and nearly all use private providers to recruit, particularly for therapeutic foster care (TFC) services, in which parents receive training and support to care for children who need a higher level of care. Recruitment strategies include searching for relatives, conducting outreach to the community, targeting certain populations, and obtaining referrals from current foster families. In response to GAO's national survey, 49 states reported using private providers to recruit foster families. In the three selected states where GAO conducted interviews, private providers were responsible for both recruiting and retaining foster families, such as helping families become licensed and providing them with support (see fig.).
Examples of Responsibilities for Private Providers, As Reported in Three States
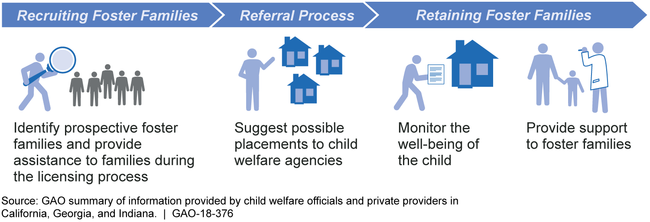
States reported various challenges with recruiting and retaining foster families in response to GAO's survey. In recruiting families, over two-thirds of states reported challenges such as limited funding and staff, which can make prioritizing recruitment efforts difficult; extensive licensing processes; and difficulties finding families willing to care for certain children, such as those with high needs. In retaining families, 29 states reported concerns about inadequate support for foster families, which can include difficulties contacting child welfare agency caseworkers. In addition, 31 states reported limited access to services needed to care for children, such as child care.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) provides a number of supports to help states recruit and retain foster families, including technical assistance with their recruitment programs, guidance and information, and funding. Most states GAO surveyed found HHS's supports moderately or very helpful. However, several private providers GAO interviewed in three selected states said they have not received guidance or information from child welfare agencies about recruiting and retaining foster families. In addition, 11 of the 14 providers said they were unaware of related HHS supports and all of them described concerns about communication with child welfare agencies. HHS officials said they encourage states to involve all relevant stakeholders in their efforts, though HHS has focused on supporting child welfare agencies. Consistent with internal control standards on communication, determining whether information on working with private providers would be useful to states could help HHS better support states' use of private providers in efforts to recruit and retain foster families.
Why GAO Did This Study
Foster care caseloads have increased in recent years due, in part, to the national opioid epidemic. States have struggled to find foster families for children who can no longer live with their parents, including those who need TFC services. States may use private providers, such as non-profit and for-profit organizations, to help recruit and retain foster families. States may also use federal funds provided by HHS for these efforts. GAO was asked to review states' efforts to recruit and retain foster families.
This report examines: (1) how state child welfare agencies recruit foster families, including those who provide TFC services, (2) any challenges in recruiting and retaining foster families, and (3) the extent to which HHS provides support to child welfare agencies in these efforts. GAO reviewed relevant federal laws, regulations, and guidance; interviewed HHS officials; surveyed child welfare agencies in all states and the District of Columbia; held discussion groups with private providers and foster parents who provide TFC services; and conducted interviews with officials in California, Georgia, and Indiana, which were selected for factors such as changes in foster care caseloads, opioid abuse rates, and geographic location.
Recommendations
GAO recommends HHS seek feedback from states on whether information on effective ways to work with private providers to recruit and retain foster families would be useful and if so, provide such information. HHS agreed with GAO's recommendation.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Health and Human Services | The Secretary of Health and Human Services should seek feedback from states on whether information on effective ways to work with private providers to recruit and retain foster families would be useful and if so, provide such information. For example, HHS can seek feedback from states through technical assistance and peer-to-peer networking activities. If states determine that information would be useful, examples of HHS actions could include facilitating information sharing among states on successful partnerships between states and private providers and encouraging states to share existing federal guidance and information. (Recommendation 1) |
In July 2018, HHS sought feedback from states about the need for information on effective ways to work with private providers and provided a forum for sharing such information. Specifically, it held an in-person, peer-to-peer meeting for state foster care managers, where managers emphasized the need for increased collaboration with private providers in recruiting and retaining foster families and shared state and local examples of collaborations. These included partnerships with private providers to develop recruitment plans and implement activities; improvements to the collection, analysis, and sharing of data on children in foster care; collaborations to adopt universal messaging used by all providers to recruit foster families; and partnerships to implement new strategies for increasing foster family retention and supports.
|
