Commercial Real Estate Lending: Banks Potentially Face Increased Risk; Regulators Generally Are Assessing Banks' Risk Management Practices
Highlights
What GAO Found
While the commercial real estate (CRE) sector has recovered since the 2007–2009 financial crisis, GAO's trend and econometric analyses generally indicate that risk in CRE lending by banks has increased over the past several years. Since the early 2000s, community banks have tended toward providing CRE loans more than other kinds of loans. Indicators of CRE market conditions and loan performance have been improving since 2011. At the same time, GAO's analyses of changes in CRE underwriting standards, property prices, and other data suggest that credit and concentration risks have increased in bank CRE lending. For example, the number of banks with relatively high CRE concentrations—measured by the ratio of a bank's CRE loans to its total capital—has been increasing. In addition, commercial property prices have been increasing rapidly, and property valuations also have risen in recent years. Similarly, GAO's predictive econometric models of CRE loan performance suggest that risk has increased, based largely on the simultaneous increase in bank CRE lending and CRE prices observed over the last several years, but is lower than the level associated with the 2007–2009 financial crisis.
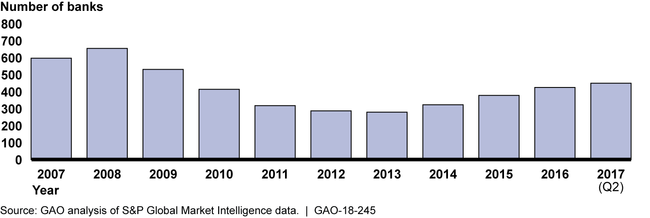
Number of Banks with Commercial Real Estate Loans Representing 300 Percent or More of Their Total Capital, Based on Year-End Data, 2007–2017
GAO found that federal banking regulators subjected banks with relatively high CRE concentrations to greater supervisory scrutiny based on its review of a nongeneralizable sample of 54 bank examinations covering 40 banks done by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, and Office of the Comptroller of the Currency from 2013 through 2016. Of the 54 examinations that GAO reviewed, 41 of them covered banks with relatively high CRE concentrations. In all of these examinations, regulators examined whether the banks had adequate risk management practices and capital to manage their CRE concentration risk. In 26 of the 41 examinations, regulators did not find any risk management weaknesses. However, in 15 of the 41 examinations, regulators found the banks had weaknesses in one or more risk management areas, such as board and management oversight, management information systems, or underwriting. The regulators generally communicated their findings to the banks in the reports of examination and directed the banks to correct their risk management weaknesses.
Why GAO Did This Study
In 2006, federal banking regulators jointly issued guidance that described their expectations for sound risk management practices for banks with CRE concentrations. The guidance includes two CRE thresholds that regulators use to identify banks that are potentially exposed to significant CRE concentration risk and could be subject to greater supervisory scrutiny. Concentrations in CRE loans at U.S. banks have been steadily increasing—raising safety and soundness concerns. In December 2015, the regulators jointly issued a public statement to remind banks of the 2006 CRE guidance.
In light of the joint 2015 statement and GAO's ongoing monitoring of regulatory efforts to identify and respond to emerging threats to the banking system, GAO examined (1) trends in the CRE lending market, including changes in risk, and (2) actions taken by regulators to help ensure that banks with CRE concentrations are effectively managing the related risks. To address these issues, GAO analyzed CRE-related data; reviewed agency policies and guidance; and reviewed a nongeneralizable sample of 54 bank examinations conducted from 2013 through 2016 based on the banks' CRE concentrations, total assets, primary regulator, and geographic location. GAO also interviewed officials from the federal banking regulators.
For more information, contact Lawrance Evans at (202) 512-8678 or evansl@gao.gov.
