Troubled Asset Relief Program: Treasury Continues to Wind down Most Programs, but Housing Programs Remain Active
Highlights
What GAO Found
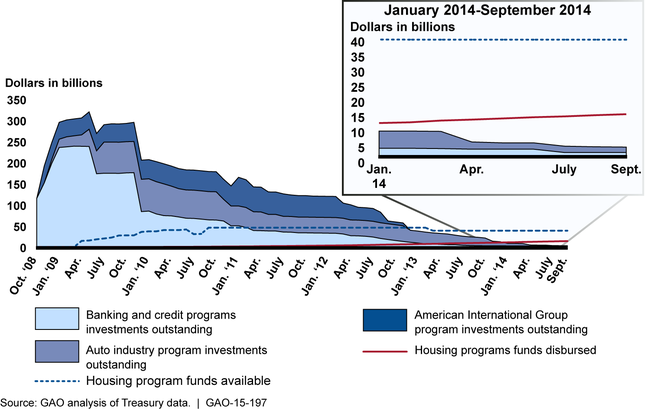
The Department of the Treasury (Treasury) continues to wind down Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) nonhousing programs that were designed to support financial and automotive markets (see figure). As of September 30, 2014, Treasury had exited four of the nine nonhousing programs that were once active, and was managing assets totaling $2.9 billion under those remaining. Some programs have yielded returns that exceed the original investment. For example, as of September 30, 2014, repayments and income from participants in the Capital Purchase Program, which provided capital to over 700 financial institutions, had exceeded original investments. In contrast, as of the same date Treasury had recouped 86 percent of its expenditures and incurred an estimated lifetime cost of $12.2 billion for the Automotive Industry Finance Program, which invested in major domestic automakers to prevent a significant industry disruption. Treasury's decision to fully exit a program depends on various factors, including the participating institutions' health and market conditions.
TARP-funded housing programs, which focus on preventing avoidable foreclosures, are ongoing. As of September 30, 2014, Treasury had disbursed $13.7 billion (36 percent) of the $38.5 billion in TARP housing funds (see figure). The number of new Home Affordable Modification Program (HAMP) permanent modifications added on a monthly basis rose in early 2013 but fell in 2014 to the lowest level since the program's inception. According to Treasury, this decline is attributable in part to the shrinking pool of eligible mortgages, as evidenced in the declining number of 60-day-plus delinquencies reported by the industry. Treasury has taken steps to help more borrowers, including by extending the deadline for program applications for a third time until at least 2016. Also, Treasury launched a new series of public service advertisements that were distributed through a donated media campaign.
Status of TARP Programs, October 2008 to September 2014
Why GAO Did This Study
The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 (EESA) authorized Treasury to create TARP, designed to restore liquidity and stability to the financial system and to preserve homeownership by assisting borrowers struggling to make their mortgage payments. Congress reduced the initial authorized amount of $700 billion to $475 billion as part of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. EESA also required that GAO report every 60 days on TARP activities in the financial and mortgage sectors. This report provides an update on the condition of all TARP programs—nonhousing and housing—as of September 30, 2014.
To conduct this work, GAO analyzed audited financial data for various TARP programs; reviewed documentation such as press releases, and agency reports on TARP programs; and interviewed Treasury officials.
GAO provided a draft of this report to Treasury. Treasury generally concurred with GAO's findings and provided technical comments, which GAO has incorporated, as appropriate.
GAO makes no recommendations in this report.
For more information, contact A. Nicole Clowers at (202) 512-8678 or clowersa@gao.gov.
