Private Health Insurance: In Most States and New Exchanges, Enrollees Continued to be Concentrated among Few Issuers in 2014 [Reissued on February 14, 2017]
Highlights
What GAO Found
GAO found that enrollment in private health insurance plans remained concentrated among a small number of issuers in most states in 2014, including in the newly established exchanges. On average in each state and the District of Columbia, 11 or more issuers participated in each of three types of markets—individual, small group, and large group—from 2011 through 2014. However, in most states, the 3 largest issuers in each market had at least an 80 percent share of the market during the period. Beginning in 2014, issuers in the individual and small group markets could sell coverage through exchanges established by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA). Not all issuers in these overall markets participated in the exchanges, and several had fewer than 3 issuers participating. Enrollment through these exchanges was generally more concentrated among a few issuers than was true for the overall markets. GAO did not assess the effect of the law on concentration and participation as 2014 was the first year of implementation for certain PPACA insurance reforms.
The Number of States Where Enrollment in the Three Largest Issuers Was at Least 80 Percent of the Market, by Market, 2011-2014
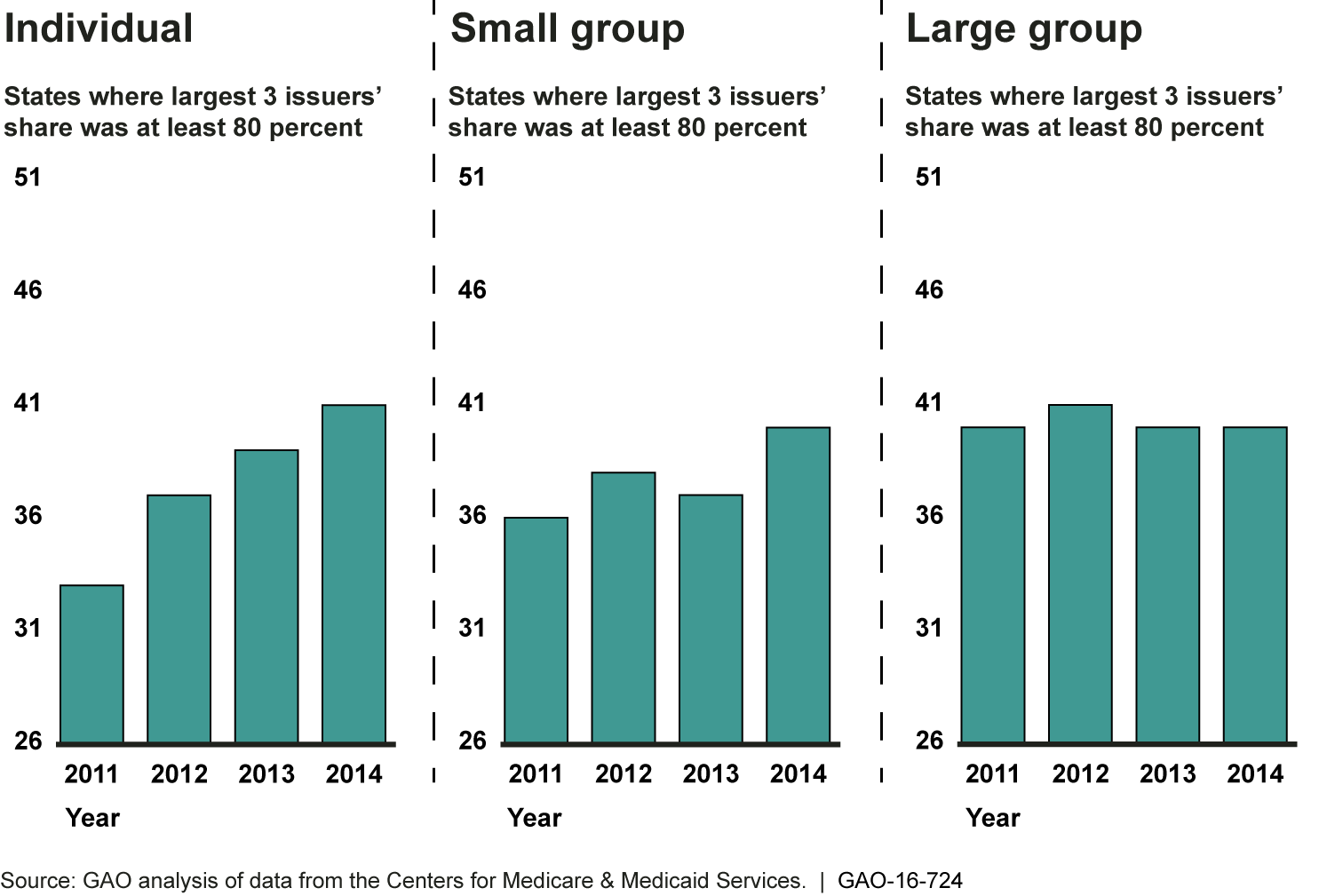
In nearly all states, the number of issuers participating in individual markets decreased from 2013 to 2014, while fewer states' small group and large group markets had decreased participation. However, across the three markets, those issuers exiting each state market before 2014 generally had less than 1 percent of the market in the prior year. There were also issuers that newly entered state markets in 2014. Their market shares in 2014 varied across the three types of markets, with some entering issuers in the individual market capturing a market share of over 10 percent. Newly entering issuers generally captured a larger share of the enrollment sold through the exchanges than through the overall markets, and some captured a majority of their exchange market.
GAO received technical comments on a draft of this report from the Department of Health and Human Services and incorporated them as appropriate.
Why GAO Did This Study
GAO previously reported that, from 2010 through 2013, enrollment in most states was concentrated among the largest issuers in each of the three types of health insurance markets: the individual, small group, and large group markets. A highly concentrated market may indicate a less competitive market and could affect consumers' choice of health plans and their premiums. In 2014, PPACA required the establishment of health insurance exchanges—a new type of market where individuals and small groups can compare and select among insurance plans—and the introduction of other reforms that could affect market concentration and competition among issuers.
PPACA included a provision for GAO to study market concentration and competition, including an analysis of newly entering issuers. In this report, GAO describes: (1) concentration in these markets in each state from 2011 through 2014 and (2) changes in issuer participation in these markets in each state from 2013 to 2014.
GAO determined market share using enrollment data from the 2011 through 2014 Medical Loss Ratio datasets that issuers are required to report annually to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). To obtain 2014 enrollment data for the issuers in the individual and small group exchanges, GAO analyzed Unified Rate Review data that certain issuers are required to report to CMS. For both datasets, enrollment for each issuer is available only at the state level and 2014 data are the most recent available.
For more information, contact John Dicken at (202) 512-7114 or dickenj@gao.gov.
